Combinatorial game theory
Combinatorial game theory (CGT) is a branch of applied mathematics and theoretical computer science that studies sequential games with perfect information, that is, two-player games which have a position in which the players take turns changing in defined ways or moves to achieve a defined winning condition. CGT does not study games with imperfect or incomplete information (sometimes called games of chance, like poker). It restricts itself to games whose position is public to both players, and in which the set of available moves is also public (perfect information).[1] Combinatorial games include well-known games like chess, checkers, Go, Arimaa, Hex, and Connect6. They also include one-player combinatorial puzzles, and even no-player automata, like Conway's Game of Life.[2] In CGT, the moves in these games are represented as a game tree.
Game theory in general includes games of chance, games of imperfect knowledge, and games in which players can move simultaneously, and they tend to represent real-life decision making situations. CGT has a different emphasis than "traditional" or "economic" game theory, which was initially developed to study games with simple combinatorial structure, but with elements of chance (although it also considers sequential moves, see extensive-form game). Essentially, CGT contributed new methods for analyzing game trees, for example using surreal numbers, which are a subclass of all two-player perfect-information games.[2] The type of games studied by CGT is also of interest in artificial intelligence, particularly for automated planning and scheduling. In CGT there has been less emphasis on refining practical search algorithms (like the alpha-beta pruning heuristic, included in most artificial intelligence textbooks today), but more emphasis on descriptive theoretical results, like measures of game complexity or proofs of optimal solution existence without necessarily specifying an algorithm (see strategy-stealing argument for instance).
An important notion in CGT is that of solved game (which has several flavors), meaning for example that one can prove that the game of tic-tac-toe results in a draw if both players play optimally. While this is a trivial result, deriving similar results for games with rich combinatorial structures is difficult. For instance, in 2007 it was announced that checkers has been (weakly, but not strongly) solved—optimal play by both sides also leads to a draw—but this result was a computer-assisted proof.[3] Other real world games are mostly too complicated to allow complete analysis today (although the theory has had some recent successes in analyzing Go endgames). Applying CGT to a position attempts to determine the optimum sequence of moves for both players until the game ends, and by doing so discover the optimum move in any position. In practice, this process is tortuously difficult unless the game is very simple.
Contents |
History
CGT arose in relation to the theory of impartial games, in which any play available to one player must be available to the other as well. One very important such game is nim, which can be solved completely. Nim is an impartial game for two players, and subject to the normal play condition, which means that a player who cannot move loses. In the 1930s, the Sprague-Grundy theorem showed that all impartial games are equivalent to heaps in nim, thus showing that major unifications are possible in games considered at a combinatorial level (in which detailed strategies matter, not just pay-offs).
In the 1960s, Elwyn R. Berlekamp, John H. Conway and Richard K. Guy jointly introduced the theory of a partisan game, in which the requirement that a play available to one player be available to both is relaxed. Their results were published in their book Winning Ways for your Mathematical Plays in 1982. However, the first book published on the subject was Conway's On Numbers and Games, also known as ONAG, which introduced the concept of surreal numbers and the generalization to games. On Numbers and Games was also a fruit of the collaboration between Berlekamp, Conway, and Guy.
Combinatorial games are generally, by convention, put into a form where one player wins when the other has no moves remaining. It is easy to convert any finite game with only two possible results into an equivalent one where this convention applies. One of the most important concepts in the theory of combinatorial games is that of the sum of two games, which is a game where each player may choose to move either in one game or the other at any point in the game, and a player wins when his opponent has no move in either game. This way of combining games leads to a rich and powerful mathematical structure.
John Conway states in ONAG that the inspiration for the theory of partisan games was based on his observation of the play in go endgames, which can often be decomposed into sums of simpler endgames isolated from each other in different parts of the board.
Examples
The introductory text Winning Ways introduced a large number of games, but the following were used as motivating examples for the introductory theory:
- Blue-Red Hackenbush - At the finite level, this partisan combinatorial game allows constructions of games whose values are dyadic rational numbers. At the infinite level, it allows one to construct all real values, as well as many infinite ones which fall within the class of surreal numbers.
- Blue-Red-Green Hackenbush - Allows for additional game values that are not numbers in the traditional sense, for example, star.
- Toads and Frogs - Allows various game values. Unlike most other games, a position is easily represented by a short string of characters.
- Domineering - Various interesting Games, such as hot games, appear in Domineering, because there is sometimes an incentive to move, and sometimes not. This allows discussion of a game's temperature.
- Nim - An impartial game. This allows for the construction of the nimbers. (It can also be seen as a green-only special case of Blue-Red-Green Hackenbush.)
The classic game Go was influential on the early combinatorial game theory, and Berlekamp and Wolfe subsequently developed an endgame and temperature theory for it (see references). Armed with this they were able to construct plausible Go endgame positions from which they could give expert Go players a choice of sides and then defeat them either way.
Overview
A game, in its simplest terms, is a list of possible "moves" that two players, called left and right, can make. The game position resulting from any move can be considered to be another game. This idea of viewing games in terms of their possible moves to other games leads to a recursive mathematical definition of games that is standard in combinatorial game theory. In this definition, each game has the notation {L|R}. 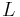 is the set of game positions that the left player can move to, and
is the set of game positions that the left player can move to, and 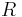 is the set of game positions that the right player can move to; each position in L and R is defined as a game using the same notation.
is the set of game positions that the right player can move to; each position in L and R is defined as a game using the same notation.
Use Domineering as an example, label each of the sixteen boxes of the four-by-four board by A1 for the upper leftmost square, C2 for the third box from the left on the second row from the top, and so on. We use e.g. (D3, D4) to stand for the game position in which a vertical domino has been placed in the bottom right corner. Then, the initial position can be described in combinatorial game theory notation as
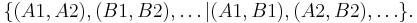 |
Note that, in standard Cross-Cram play, the players alternate turns, but this alternation is handled implicitly by the definitions of combinatorial game theory rather than being encoded within the game states.
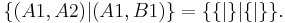 |
The above game (an irrelevant open square at C3 has been omitted from the diagram) describes a scenario in which there is only one move left for either player, and if either player makes that move, that player wins. The {|} in each player's move list (corresponding to the single leftover square after the move) is called the zero game, and can actually be abbreviated 0. In the zero game, neither player has any valid moves; thus, the player whose turn it is when the zero game comes up automatically loses.
The type of game in the diagram above also has a simple name; it is called the star game, which can also be abbreviated *. In the star game, the only valid move leads to the zero game, which means that whoever's turn comes up during the star game automatically wins.
An additional type of game, not found in Domineering, is a loopy game, in which a valid move of either left or right is a game which can then lead back to the first game. Checkers, for example, becomes loopy when one of the pieces promotes, as then it can cycle endlessly between two or more squares. A game that does not possess such moves is called nonloopy.
Game Abbreviations
Numbers
Numbers represent the number of free moves, or the move advantage of a particular player. By convention positive numbers represent an advantage for Left, while negative numbers represent an advantage for Right. They are defined recursively with 0 being the base case.
- 0 = {|}
- 1 = {0|}, 2 = {1|}, 3 = {2|}
- -1 = {|0}, -2 = {|-1}, -3 = {|-2}
The zero game is a loss for the first player.
The sum of number games behaves like the integers, for example 3 + -2 = 1.
Star
Star, written as * or {0|0}, is a first-player win since either player must (if first to move in the game) move to a zero game, and therefore win.
- * + * = 0, because the first player must turn one copy of * to a 0, and then the other player will have to turn the other copy of * to a 0 as well; at this point, the first player would lose, since 0 + 0 admits no moves.
The game, *, is neither positive nor negative; it and all other games in which the first player wins (regardless of which side the player is on) are said to be fuzzy with or confused with 0; symbolically, we write * || 0.
Up
Up, written as ↑, is a position in combinatorial game theory.[4] In standard notation, ↑ = {0|*}.
- −↑ = ↓ (down)
Up is strictly positive (↑ > 0), but is infinitesimal. Up is defined in Winning Ways for your Mathematical Plays.
Down
Down, written as ↓, is a position in combinatorial game theory.[4] In standard notation, ↓ = {*|0}.
- −↓ = ↑ (up)
Down is strictly negative (↓ < 0), but is infinitesimal. Down is defined in Winning Ways for your Mathematical Plays.
"Hot" games
Consider the game {1|-1}. Both moves in this game are an advantage for the player who makes them; so the game is said to be "hot;" it is greater than any number less than -1, less than any number greater than 1, and fuzzy with any number in between. It is written as ±1. It can be added to numbers, or multiplied by positive ones, in the expected fashion; for example, 4 ± 1 = {5|3}.
Nimbers
An impartial game is one where, at every position of the game, the same moves are available to both players. For instance, Nim is impartial, as any set of objects that can be removed by one player can be removed by the other. However, domineering is not impartial, because one player places horizontal dominoes and the other places vertical ones. Likewise Checkers is not impartial, since the players move different pieces. For any ordinal number, one can define an impartial game generalizing Nim in which, on each move, either player may replace the number with any smaller ordinal number; the games defined in this way are known as nimbers. The Sprague–Grundy theorem states that every impartial game is equivalent to a nimber.
The "smallest" (simplest, and least under the usual ordering of the ordinals) nimbers are 0 and *.
See also
- Alpha-beta pruning
- Backward induction
- Connection game
- Expectiminimax tree
- Extensive-form game
- Game complexity
- Go (board game)
- Grundy's game
- Multi-agent system
- Sylver coinage
- Wythoff's game
- Topological game
- Zugzwang
Notes
- ^ Lessons in Play, p. 3
- ^ a b http://erikdemaine.org/papers/AlgGameTheory_GONC3/paper.pdf
- ^ Schaeffer, J.; Burch, N.; Björnsson, Y.; Kishimoto, A.; Müller, M.; Lake, R.; Lu, P.; Sutphen, S. (2007). "Checkers is solved". Science 317 (5844): 1518–1522. Bibcode 2007Sci...317.1518S. doi:10.1126/science.1144079. PMID 17641166. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.95.5393&rep=rep1&type=pdf.
- ^ a b E. Berlekamp, J. H. Conway, R. Guy (1982). Winning Ways for your Mathematical Plays. Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-091101-9, ISBN 0-12-091102-7.
References
- Albert, Michael H.; Nowakowski, Richard J.; Wolfe, David (2007). Lessons in Play: In Introduction to Combinatorial Game Theory. A K Peters Ltd. ISBN 978-1-56881-277-9.
- Beck, József (2008). Combinatorial games: tic-tac-toe theory. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521461009. http://books.google.com/books?id=AU4dh_eKNfkC.
- Berlekamp, E.; Conway, J. H.; Guy, R. (1982). Winning Ways for your Mathematical Plays. Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-091101-9, ISBN 0-12-091102-7. 2nd ed., A K Peters Ltd (2001–2004), ISBN 1-56881-130-6, ISBN 1-56881-142-X, ISBN 1-56881-143-8, ISBN 1-56881-144-6.
- Berlekamp, Elwyn; Wolfe, David (1997). Mathematical Go: Chilling Gets the Last Point. A K Peters Ltd. ISBN 1-56881-032-6.
- Bewersdorff, Jörg (2004). Luck, Logic and White Lies: The Mathematics of Games. A K Peters Ltd. ISBN 1-56881-210-8. See especially sections 21–26.
- Conway, John Horton (1976). On Numbers and Games. Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-186350-6. 2nd ed., A K Peters Ltd (2001), ISBN 1-56881-127-6.
- Robert A. Hearn; Erik D. Demaine (2009). Games, Puzzles, and Computation. A K Peters, Ltd.. ISBN 9781568813226.
External links
- List of combinatorial game theory links at the homepage of David Eppstein
- An Introduction to Conway's games and numbers by Dierk Schleicher and Michael Stoll
- Combinational Game Theory terms summary by Bill Spight
- Combinatorial Game Theory Workshop, Banff International Research Station, June 2005